Three Phase Transformer
In many countries, three-phase power is used for industrial electricity supply, but the voltage and frequency vary by country. For example, in Japan, three-phase power of 200V at 50Hz/60Hz is commonly used, while in other countries, 400V or different frequencies are more prevalent. When exported industrial machines do not conform to the local voltage or frequency, a three-phase transformer is required to convert the power appropriately.
By using a three-phase transformer, high-load industrial machines designed for Japanese domestic specifications (such as CNC machines, lathes, and milling machines) can be exported overseas and operated without modifying their specifications. An isolation transformer physically separates the primary and secondary sides, providing protection for equipment and workers from overcurrent and short circuits.
Standard Specifications
- Compliance: IEC 61558-1/A1:2009, IEC 61558-2-4:2009
- Certification: Autotransformer: TUV-SUD/261862
Isolation Transformer: TUV-SUD/261910 - Primary and Secondary Voltage Range: Up to 500V
- Max Capacity: Up to 400 kVA
- Wiring Material: Copper wire / Aluminum wire
- Silicon Steel Sheets: High-quality non-oriented electrical steel and low-loss grain-oriented electrical steel are used.
- Insulation Class: Class F / H
- Ambient Temperature: Maximum ambient temperature: 40°C
- IP Protection Rating: Compliant with IP33 (Other ratings available upon request) High Efficiency

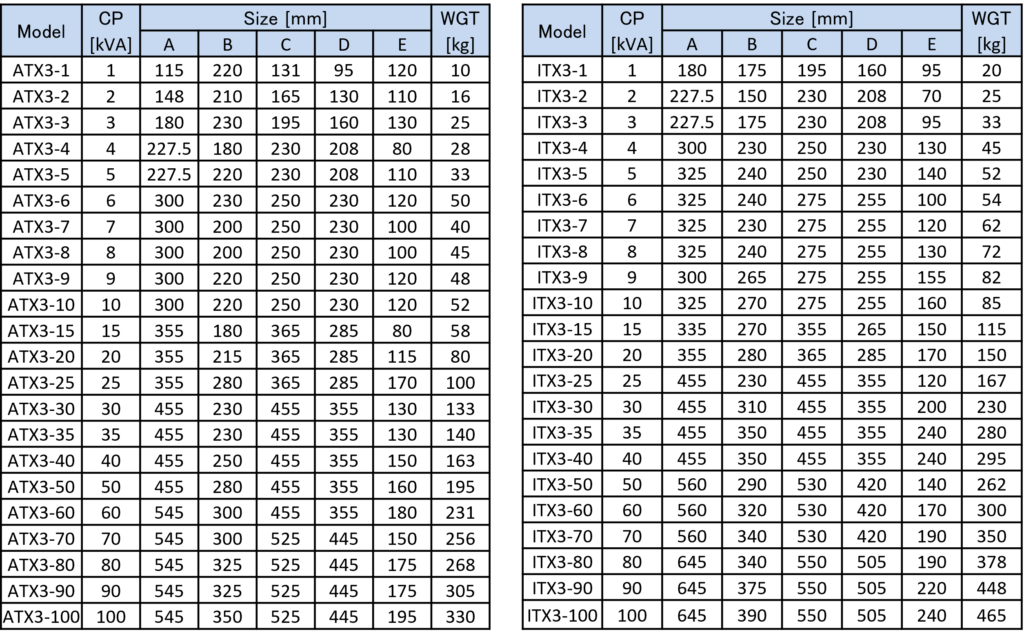
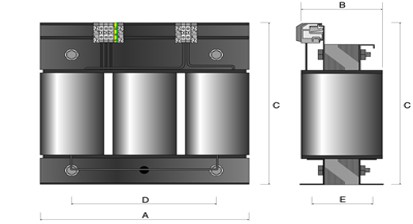
Dimensional Specifications
Reactor
A reactor functions as an inductor (coil) in electrical circuits and is used to control changes in current or voltage. It is widely used across various fields, particularly for noise suppression, voltage fluctuation smoothing, or circuit protection.
Features
- Excellent Noise Suppression Performance
Reactors are effective in blocking or attenuating high-frequency noise, enhancing the operational stability of equipment. In particular, by mitigating the impact of noise generated in power circuits and inverter circuits, reactors prevent interference with peripheral devices. - Current Control and Energy Storage
Reactors help protect circuits from transient currents by smoothing sudden changes in current. Additionally, they utilize inductance to temporarily store energy, contributing to power smoothing.