Toroidal Transformer
A toroidal transformer is a type of power transformer with a structure where electrical wires are directly wound around a continuous, donut-shaped iron core.
It offers excellent electrical characteristics, including high efficiency, low losses, and low magnetic leakage, making it ideal for use in high-quality devices.
Features
- High Efficiency
Due to the continuous closed magnetic path formed by the core, magnetic losses are minimized, achieving high conversion efficiency. - Low Magnetic Leakage
The design confines the magnetic flux within the core, minimizing magnetic leakage and reducing interference with surrounding electronic devices. - Compact and Lightweight
Compared to EI transformers, toroidal transformers can be designed to be more compact and lightweight for the same output capacity. - Low Noise
The windings uniformly surround the core, suppressing electromagnetic noise and vibrations. - High Manufacturing Cost
The winding process is complex and labor-intensive, leading to higher manufacturing costs. - Not Suitable for Mass Production
The manufacturing process is difficult to automate and relies heavily on manual labor, making it less suitable for mass production.
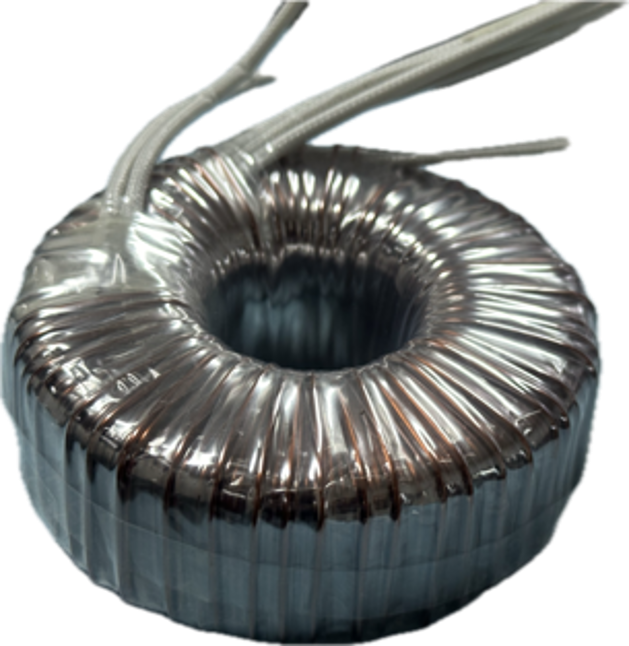

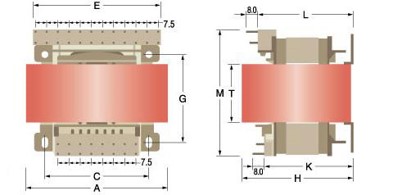
Dimensional Specifications
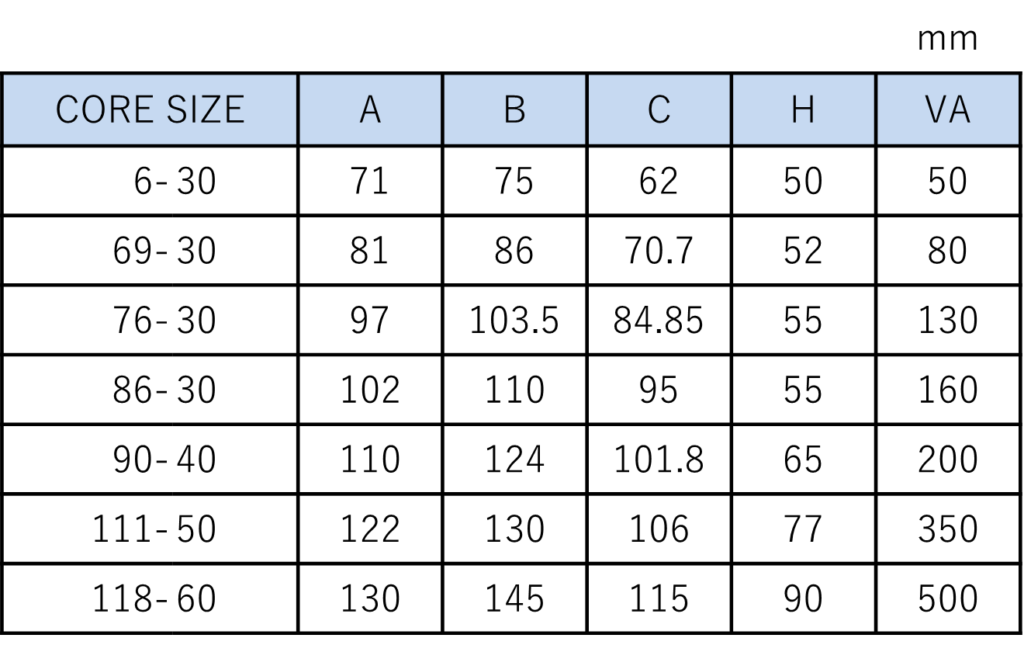
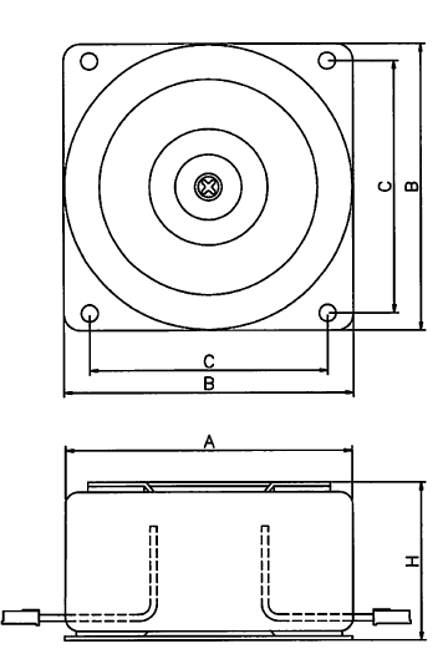
EI Transformer
An EI transformer is a type of power transformer constructed with an E-shaped and I-shaped iron core (core) and copper wire wound on a bobbin. It operates stably over a wide frequency range, is resistant to magnetic saturation, and is suitable for handling high currents. Compared to toroidal transformers, its simpler structure allows for reduced manufacturing costs.
Features
- Low Manufacturing Cost
The simple structure and straightforward manufacturing process help reduce production costs. - Suitable for Mass Production
Standardized components and processes allow for efficient mass production. - Design Flexibility
The use of a bobbin makes it relatively easy to modify the winding and core design. - High Magnetic Leakage
Due to the core’s structure, magnetic flux is more likely to leak externally, potentially affecting nearby equipment. - Low Efficiency
Magnetic losses are higher compared to toroidal transformers, which can result in lower conversion efficiency. - Prone to Noise
Magnetic leakage and vibrations tend to increase electromagnetic noise.
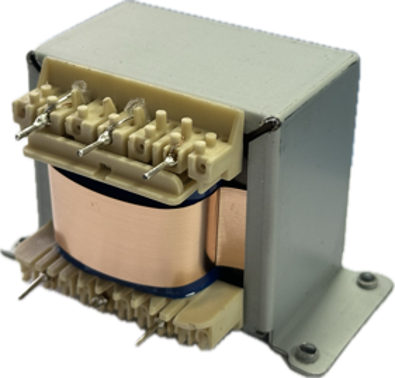
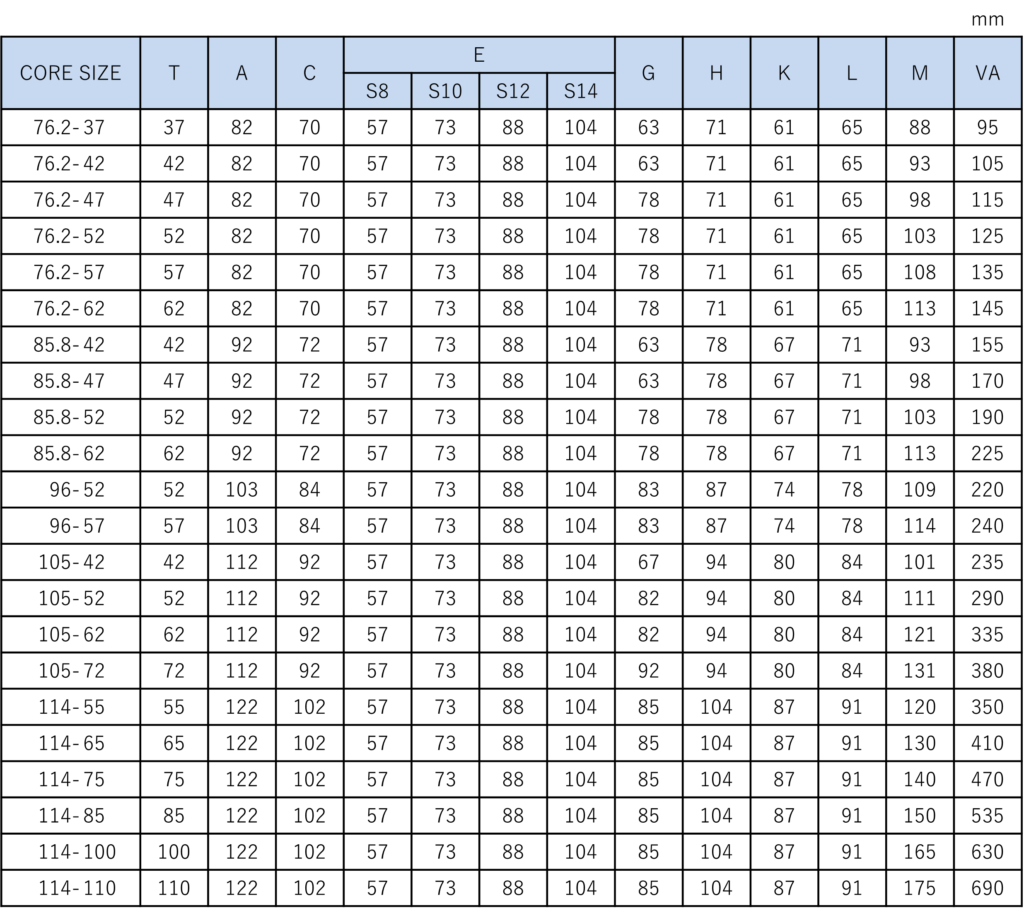
Dimensional Specifications
Power Transformers for High-End Audio Equipment
PREMIUM BANDO

An immersive experience as if you were in a forest, listening to the chirping of birds.
A sense of sonic transparency that makes you forget the existence of machinery.
PREMIUM BANDO is a power transformer for high-end audio equipment, developed to fully reproduce the true allure of music.
At BANDO, through the development and production of PREMIUM BANDO, we aim to preserve and advance the audio technology and craftsmanship that countless predecessors in Japan have devoted themselves to creating, passing it on to future generations.